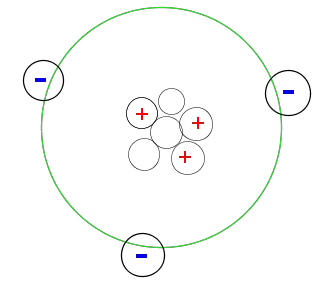
In an electrically neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of - YouTube

Overscreening, Co-Ion-Dominated Electroosmosis, and Electric Field Strength Mediated Flow Reversal in Polyelectrolyte Brush Functionalized Nanochannels | ACS Nano

Atomic Structure. What is an atom? An atom is an electrically neutral, spherical entity. It is comprised of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by. - ppt download

Boosting the performance of single-atom catalysts via external electric field polarization | Nature Communications

An early model for an atom considered it to have a positively charged point nucleus of charge Ze , surrounded by a uniform density of negative charge upto a radius R .
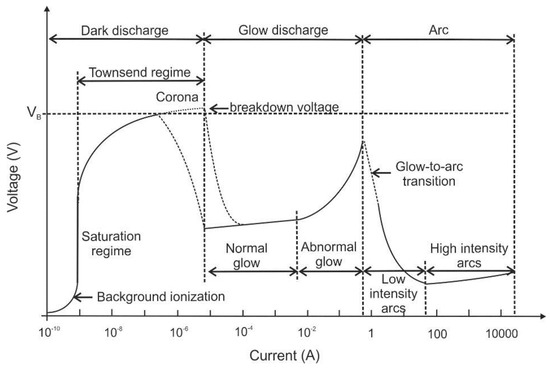
Energies | Free Full-Text | Overview of Electric Field Applications in Energy and Process Engineering

Effect of electric field intensity on electrophoretic migration and deformation of oil droplets in O/W emulsion under DC electric field: A molecular dynamics study - ScienceDirect
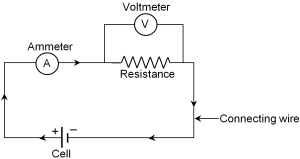
Properties of Electric current, Simple electric circuit, Current intensity & Potential difference | Science online